COVID-19 and Herpes Zoster Co-infections Identified
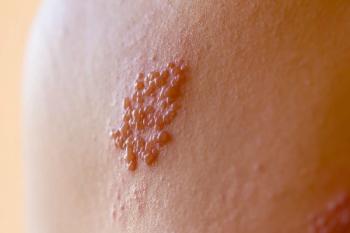
Reports of cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and herpes zoster co-infections are beginning to emerge in medical literature.
Reports of cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (
The first study, published in the
The patient’s medical history included 2 possible exposures to COVID-19 during the month of March: a cruise and the arrival of a friend from the United States. A subsequent COVID-19 test was positive.
Intravenous acyclovir was initiated to treat his shingles, and clinical improvement was seen within 24 hours. The progression of HZ lesions ceased by the fifth day, and the patient was also free of fever and respiratory symptoms.
“COVID‐19 might have fostered retrograde reactivation of VZV from the nasal cavity, where ophthalmic and maxillary branches of the trigeminal nerve are harboured,” the researchers concluded. “Hence, COVID‐19 might also entail this rare presentation of HZ.”
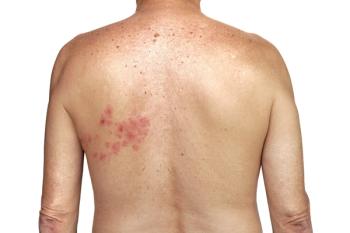
The October 2020 issue of the
The patients were all immunocompetent and had mild-to-moderate COVID-19 at the onset of HZO, but did not require hospitalization. The mean time between the onset of COVID-19 and the HZO diagnosis was 4.5 days.
The treating physicians noted that the usual
“It seems that COVID‐19 infection, as an acute illness with its associated physical and emotional stress, might represent the triggering factor for the development of HZO in our patients,” they wrote.
All 4 patients were treated with systemic and topical acyclovir and topical prednisolone acetate eye drops. No ocular complications or postherpetic neuralgia (
“In conclusion, cutaneous manifestations of COVID‐19 disease are continuously emerging,” the physicians wrote. “HZO might be a complication to or an indicator of COVID‐19 infection, particularly in young, immunocompetent patients.”
Given the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, individuals at highest risk should consider vaccination against shingles. “Ensuring that routine vaccination is maintained or reinitiated during the COVID-19 pandemic is essential for protecting individuals and communities from vaccine-preventable diseases and outbreaks,” states the
The
References
1. Ferreira ACA de F. Romão TT. Macedo YS. Pupe C, Nascimento OJM. COVID-19 and herpes zoster co-infection presenting with trigeminal neuropathy. European Journal of Neurology. 2020.
2. Nofal A, Fawzy MM, Sharaf EL Deen SM, El-Hawary EE. Herpes zoster ophthalmicus in COVID-19 patients. 2020.
3. CDC. Interim Guidance for Routine and Influenza Immunization Services During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Last updated October 20, 2020. Accessed December 1, 2020.
4. Immunization Action Coalition. COVID-19 and Routine Vaccination. Last updated October 22, 2020. Accessed December 1, 2020.
Newsletter
Pharmacy practice is always changing. Stay ahead of the curve with the Drug Topics newsletter and get the latest drug information, industry trends, and patient care tips.